How to Install a Centrifugal Monoblock Pump: A Step-by-Step Guide
2024-12-05
Centrifugal monoblock pumps are single-unit pumps where the pump and motor are mounted on a common shaft, eliminating the need for coupling between them. These pumps are widely used in agricultural, industrial, and residential applications due to their simple design, efficiency, and ease of maintenance.
Centrifugal pumps work by converting rotational kinetic energy from the motor into hydrodynamic energy, allowing them to move liquids, typically water, at high flow rates.
Their compact size, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice for applications requiring continuous water circulation or transfer.
Importance of proper installation for efficiency and longevity of Centrifugal Monoblock Pump
Proper installation of a centrifugal monoblock pump is crucial for ensuring its efficiency and longevity. Here's why:
- Optimal Performance: Correct installation helps the pump operate at peak efficiency, ensuring it delivers the expected flow rate and pressure. Poor alignment or incorrect connections can cause performance losses, reducing the pump's ability to move water effectively.
- Prevention of Damage: Improper installation, such as air leaks in suction lines or incorrect priming, can cause the pump to run dry, leading to overheating, excessive wear, or impeller damage. This can shorten the lifespan of the pump.
- Energy Efficiency: A well-installed pump operates smoothly, minimizing energy consumption. Misalignments, leaks, or vibrations due to improper setup can lead to increased power usage and higher operational costs.
- Longer Lifespan: When installed correctly, the pump can run smoothly for many years, reducing wear and tear on components, and prolonging its operational life.
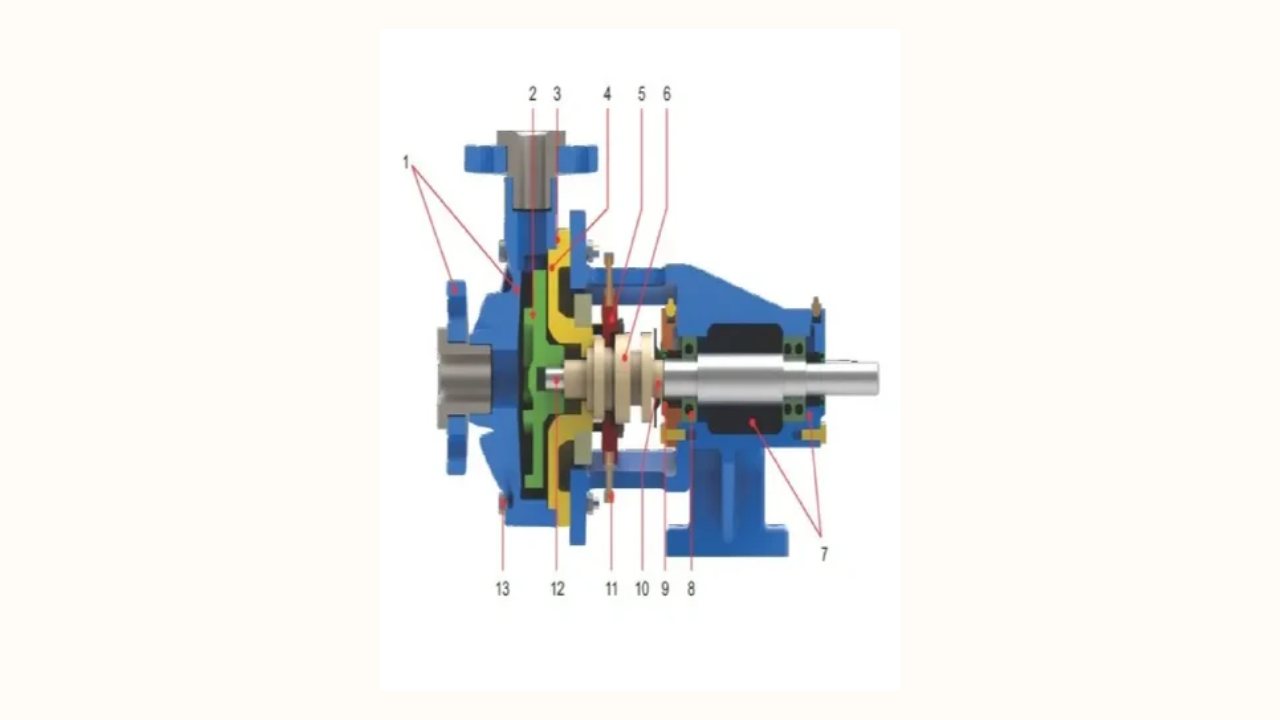
The main parts of a centrifugal pump include
- Impeller: The rotating component that transfers energy from the motor to the fluid, increasing its velocity and pressure.
- Casing: The outer shell that encloses the impeller, designed to direct fluid flow and convert velocity into pressure. It’s usually volute-shaped.
- Shaft: A rod that connects the impeller to the motor, transferring mechanical energy to the impeller.
- Seal or Packing: Prevents leakage of the fluid along the shaft where it exits the casing.
- Bearing: Supports the shaft and allows it to rotate smoothly with minimal friction.
- Suction and Discharge Nozzles: The suction nozzle allows fluid to enter the pump, and the discharge nozzle directs the fluid out at high pressure.
- Wear Rings: Installed between the impeller and casing to minimize leakage and reduce wear from contact between these parts.
Installation Steps of Centrifugal Monoblock Pump
By following these installation steps carefully, you can ensure that your centrifugal monoblock pump operates efficiently and reliably.
1. Positioning the Pump
- Choose the Right Location: Select a dry, clean, and stable surface for the pump, ideally near the water source and power supply. It should be easily accessible for future maintenance.
- Pump Mounting: Ensure the pump is firmly mounted on a flat, vibration-free foundation. If necessary, use a base plate or wooden slab to minimize vibrations and provide stability.
- Shelter From Water & Dust: Place the pump in a sheltered location to protect it from rain and excessive external elements. Exposure to rain and dust will significantly reduce the performance and life of the pump
- Ensure Adequate Ventilation: The pump motor should have adequate airflow around it to prevent overheating. Avoid placing it in a confined space without ventilation.
2. Connecting the Suction Pipe
- Measure and Cut the Pipe: Measure the correct length for the suction pipe to avoid excessive bends. Use the correct diameter according to the pump specifications.
- Install the Suction Flange: Attach the suction pipe to the pump’s suction flange using the appropriate fittings (e.g., flanged or threaded). Ensure the joint is tight to prevent air leaks, which can impair the pump’s performance.
- Check for Leaks: Before securing the pipe fully, run water through the suction pipe to check for any potential leaks. Use Teflon tape or thread sealant for threaded joints to prevent leaks.
3. Connecting the Discharge Pipe
- Measure and Cut the Discharge Pipe: Similar to the suction pipe, measure and cut the discharge pipe to avoid unnecessary bends and pressure losses.
- Attach the Discharge Flange: Secure the discharge pipe to the pump’s discharge flange. Use appropriate pipe fittings and make sure they are tight and sealed.
- Ensure Correct Alignment: Make sure the discharge pipe is aligned with the intended discharge point (e.g., water tank, irrigation system) to avoid strain on the pump.
4. Electrical Wiring and Motor Connection -
- Verify Electrical Specifications: Check the voltage and current ratings of the pump’s motor. Ensure the power supply matches these specifications.
- Turn Off Power: Ensure the power supply is off before wiring the motor.
- Connect the Power Leads: Follow the pump's wiring diagram to connect the electrical leads to the power supply. Make sure to connect the correct terminals for phase, neutral, and ground.
- Check Motor Alignment: Ensure the motor is correctly aligned with the pump shaft.
- Grounding: Properly ground the motor to prevent electric shocks or damage to the pump.
- Test Electrical Connections: After wiring, check that all electrical connections are secure and insulated. Use a multimeter to test voltage and continuity.
5. Priming the Pump
- Fill the Pump Casing: Before starting the pump, fill the pump casing with water (prime it) to prevent dry running, which can cause damage to the pump’s seals and internal components.
- Vent the Air: Open the air vent valve (if available) to expel trapped air from the system.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect all joints and pipe connections for any leaks during the priming process.
6. Testing the Pump
- Turn on the Power: Switch on the power supply and start the pump.
- Monitor Operation: Observe the pump’s operation to ensure it is running smoothly. Look out for abnormal vibrations, noise, or overheating.
- Check Flow and Pressure: Use a pressure gauge to ensure that the pump is providing the required flow rate and pressure.
- Adjust as Necessary: If the pressure or flow rate is too low, check for possible clogs, air locks, or incorrect pipe sizing. Adjust the pump speed or valve settings if needed.
7. Final Adjustments
- Tighten Connections: After the initial run, ensure all pipe connections and bolts are securely tightened, as vibrations during operation may loosen them.
- Align the Shaft: If necessary, check that the pump shaft is aligned correctly with the motor and that no misalignment is causing friction or excessive wear.
- Set Pressure Switch: If the pump is equipped with a pressure switch, adjust it according to the desired operational pressure.
Troubleshooting Common Issues When Installing a Centrifugal Monoblock Pump
One common issue during the installation of a centrifugal monoblock pump is no water flow. This could be caused by several factors, such as the pump not being primed correctly, a blockage in the suction line, or the pump impeller being damaged.
Ensure that the pump is fully primed before starting, and check for any obstructions or air pockets in the suction line. If necessary, clean the impeller or replace it if it is worn or damaged.
Excessive noise or vibrations is another frequent problem, often caused by misalignment between the motor and the pump, loose mounting, or cavitation. Ensure that the pump is properly aligned with the motor and tightly secured to the base.
Cavitation, caused by air entering the pump or insufficient flow to the impeller, can also generate noise and vibrations. This can be solved by making sure the suction line is free from air leaks and that the pump is receiving an adequate fluid supply.
Overheating of the pump typically occurs due to poor ventilation, high friction from worn bearings, or a motor overload. Check that the pump is installed in a well-ventilated area, with sufficient airflow around the motor to dissipate heat.
Additionally, inspect the bearings for wear and ensure proper lubrication. If the motor is overloaded, consider reducing the load or checking for blockages in the system that could be causing excessive strain.
Lastly, low pressure can be an issue, often due to leaks in the discharge line, a clogged impeller, or incorrect pump sizing. Inspect the discharge line for any leaks, and clean or replace the impeller if necessary.
If the pump is too small for the system’s requirements, it may not generate sufficient pressure, and a larger pump may be needed to meet performance demands.
Safety Tips and Best Practices
When installing a centrifugal monoblock pump, safety is crucial to ensure not only proper installation but also to prevent accidents. Here are key safety tips to follow:
-
Ensure the pump has adequate ventilation:
Ensure the pump is installed in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating. Adequate airflow around the pump motor is essential for dissipating heat, as lack of ventilation can reduce efficiency and damage the motor over time. It's equally important to never run the pump dry.
-
Never run the pump dry:
Before operation, make sure the pump is fully primed with water or the appropriate fluid, as dry running can severely damage internal components like seals, impellers, and bearings. Installing automatic sensors or control systems can help prevent this issue.
-
Regularly check for leaks and perform routine maintenance:
Regularly checking for leaks and performing routine maintenance is crucial for safe and efficient operation. Inspect the pump and its connections for any signs of leakage, which could indicate worn-out seals or installation problems.
Following the manufacturer's maintenance schedule will help keep components such as bearings, seals, and impellers in optimal condition. Monitoring vibration, noise, and temperature will also allow for early detection of mechanical issues, ensuring that the pump remains reliable and safe to use.
A Final Word of Advice
In conclusion, installing a centrifugal monoblock pump involves careful planning and attention to detail, from selecting the right location with proper ventilation to securely mounting the pump and ensuring it is primed before operation.
Regular checks for leaks, alignment, and proper electrical connections are essential for smooth performance. By following these steps and adhering to maintenance schedules, you can ensure efficient and long-lasting pump operation.
Search
Recent Post
-
How industrial pump suppliers ensure efficiency and longevity of equipment

Industrial pumps play a critical role in manufacturing, processing, and large-scale production. The efficiency and lifespan of these essential machines depend heavily on the quality of the pump and the support provided by the supplier.
A reliable supplier ensures that the right pump is selected, installed, and maintained properly for optimal performance and durability.
In this guide, we’ll explore how industrial pump suppliers like Calama Pumps contribute to equipment efficiency and longevity.
Understanding the Importance of Industrial Pump Efficiency and Longevity
Efficient industrial pumps reduce operational costs, minimize downtime, and enhance productivity. Longevity ensures fewer replacements and repairs, leading to long-term savings and consistent performance. High-quality suppliers prioritize both efficiency and durability to maximize the value of their products.
How Industrial Pump Suppliers Ensure Efficiency
1. Providing High-Quality Pumps
A top-tier supplier offers pumps made from durable, corrosion-resistant materials designed to handle various industrial fluids and pressures. Calama Pumps, for instance, provides robust equipment built for demanding environments.
2. Expert Consultation and Product Selection
Proper pump selection is crucial for efficiency. Suppliers assess your system’s requirements, including flow rate, pressure, and fluid type, to recommend the ideal pump model.
3. Customization Options
Some industrial applications require tailored solutions. Reliable suppliers offer customization, ensuring pumps are designed to meet specific operational needs.
4. Advanced Technology and Innovation
Modern industrial pumps feature advanced designs that improve efficiency, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) and high-efficiency impellers. Suppliers stay updated with technological advancements to offer cutting-edge products.
5. Energy Efficiency Focus
Energy-efficient pumps lower operational costs and reduce environmental impact. Suppliers guide businesses toward models with high-efficiency ratings and optimized performance.
How Industrial Pump Suppliers Ensure Longevity
1. Quality Assurance and Testing
Reputable suppliers conduct rigorous testing to ensure their pumps meet industry standards for performance and durability.
2. Comprehensive Installation Support
Proper installation is key to longevity. Suppliers provide detailed guidance and professional installation services to prevent common issues.
3. Maintenance and Service Plans
Regular maintenance extends pump life. Suppliers like Calama Pumps offer service packages, including inspections, part replacements, and performance assessments.
4. Access to Genuine Spare Parts
Using authentic parts ensures compatibility and maintains performance. Established suppliers stock a wide range of genuine components.
5. Training and Technical Support
Knowledgeable operators enhance efficiency and lifespan. Suppliers provide training programs and ongoing technical support to keep systems running smoothly.
Why Choose Calama Pumps for Industrial Solutions
Calama Pumps stands out as a trusted name in the industry, offering high-quality pumps, expert consultation, and comprehensive after-sales support. Their commitment to efficiency and longevity makes them a preferred choice for industrial operations worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is supplier selection important for pump efficiency?
The right supplier ensures you get high-quality, energy-efficient pumps tailored to your needs, reducing operational costs and enhancing performance.
How do industrial pump suppliers improve equipment longevity?
Suppliers offer quality products, proper installation, regular maintenance, and access to genuine parts, all of which extend pump life.
What role does customization play in pump efficiency?
Customized pumps match specific operational requirements, optimizing performance and minimizing wear and tear.
Why trust Calama Pumps for industrial solutions?
Calama Pumps provide durable, efficient equipment with excellent support services, ensuring long-term reliability and productivity.
How often should industrial pumps be serviced?
Regular maintenance, including inspections and part replacements, should be conducted at least annually to maintain efficiency and prevent breakdowns.
By partnering with reliable industrial pump suppliers like Calama Pumps, businesses ensure their equipment operates at peak efficiency and enjoys a long service life. Quality products, expert support, and comprehensive maintenance plans all contribute to optimal performance and cost savings over time.
-
High pressure pumps: how they work and where they are used

High-pressure pumps play a crucial role in various industrial and commercial operations. From manufacturing plants to water treatment facilities, these pumps ensure fluid movement under high pressure, enabling efficient processes and system performance.
In this detailed guide, we’ll dive into the working mechanisms of high-pressure pumps, their key applications, and why trusted suppliers like Calama Pumps offer some of the best solutions available.
Understanding High-Pressure Pumps
A high-pressure pump is designed to move liquids at significantly increased pressures compared to standard pumps. These pumps convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, generating pressure that propels fluid through pipelines and systems at high velocities.
Key Components of High-Pressure Pumps
- Pump Head: The part where the fluid enters and exits.
- Piston or Plunger: Moves back and forth to create pressure.
- Seals and Valves: Ensure fluid direction and prevent leaks.
- Motor: Provides the mechanical energy required to drive the pump.
Working Mechanism
High-pressure pumps operate by displacing a specific volume of fluid through the pump’s head using a piston, plunger, or rotating component. As the motor powers the movement, it creates pressure that pushes the liquid through the discharge line.
Types of High-Pressure Pumps
1. Reciprocating Pumps
Reciprocating pumps use pistons or plungers to displace fluid in a back-and-forth motion. These pumps are known for their precision and ability to handle high-viscosity fluids.
Applications:
- Oil and gas industry
- Chemical processing
- High-pressure cleaning systems
2. Centrifugal High-Pressure Pumps
Centrifugal pumps use rotating impellers to generate pressure through centrifugal force. They are ideal for moving large volumes of fluid quickly and efficiently.
Applications:
- Water supply systems
- HVAC systems
- Irrigation
3. Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps use flexible membranes to create pressure without direct contact between the liquid and moving parts. This makes them suitable for handling corrosive and abrasive fluids.
Applications:
- Chemical transfer
- Food and beverage industry
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
Key Applications of High-Pressure Pumps
1. Water Treatment Plants
High-pressure pumps help move water through filtration and purification systems, ensuring clean and safe water supply.
2. Manufacturing and Production
Industries rely on these pumps for cooling, lubrication, and fluid transfer processes that require consistent pressure.
3. Oil and Gas Sector
From drilling operations to pipeline transportation, high-pressure pumps manage fluid movement under extreme conditions.
4. Power Generation
In power plants, these pumps maintain cooling systems and steam production, essential for efficient energy generation.
5. Cleaning and Maintenance
High-pressure washers use these pumps for industrial cleaning, ensuring thorough removal of dirt and contaminants.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a High-Pressure Pump
1. Pressure and Flow Rate Requirements
Assess your system’s pressure needs and fluid volume to select a pump with the right capacity.
2. Fluid Type
Consider the chemical composition, temperature, and viscosity of the fluid being pumped.
3. Material and Durability
Choose pumps made from corrosion-resistant materials for longevity and reliability.
4. Energy Efficiency
Opt for high-efficiency models to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
5. Supplier Reputation
Trusted suppliers like Calama Pumps provide high-quality equipment and expert support.
Why Calama Pumps Are a Trusted Choice
Calama Pumps have established themselves as industry leaders in providing high-performance high-pressure pumps. Known for their reliability and efficiency, Calama Pumps cater to diverse industrial needs with customized solutions and exceptional after-sales support.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What industries use high-pressure pumps the most?
Industries like water treatment, oil and gas, manufacturing, and power generation rely heavily on high-pressure pumps.
How do high-pressure pumps differ from standard pumps?
High-pressure pumps generate significantly higher pressure, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Are high-pressure pumps energy-efficient?
Yes, modern high-pressure pumps are designed for efficiency, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
How do I maintain a high-pressure pump?
Regular maintenance, including seal checks, lubrication, and part replacements, ensures optimal performance.
Why choose Calama Pumps for high-pressure solutions?
Calama Pumps offer durable, efficient, and customizable high-pressure pump systems with excellent support services.
High-pressure pumps are indispensable in industrial applications requiring reliable fluid movement and consistent pressure. By partnering with reputable suppliers like Calama Pumps, businesses ensure they receive top-quality equipment tailored to their operational needs.
-
Why centrifugal pumps are the most popular choice for industrial applications

Centrifugal pumps are widely regarded as the most popular and efficient solution for industrial applications worldwide. Their simplicity, versatility, and cost-effectiveness make them the go-to choice for industries ranging from manufacturing to chemical processing.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore why centrifugal pumps are so favored and why trusted suppliers like Calama Pumps often recommend them for various industrial needs.
Understanding Centrifugal Pumps
A centrifugal pump uses rotational energy, typically from an electric motor, to move fluid through a system. The pump’s impeller spins the liquid, creating centrifugal force that pushes the fluid outward and into the discharge pipe. This simple yet effective mechanism ensures consistent fluid movement with minimal effort.
Key Components of Centrifugal Pumps:
- Impeller: The rotating component that generates centrifugal force.
- Casing: Houses the impeller and directs the flow of fluid.
- Suction Pipe: Draws fluid into the pump.
- Discharge Pipe: Expels fluid from the pump into the system.
Advantages of Centrifugal Pumps in Industrial Applications
1. High Efficiency and Performance
Centrifugal pumps are known for their ability to handle large volumes of fluid at high speeds, making them ideal for industrial operations requiring quick and efficient fluid transfer.
Benefits:
- Consistent flow rates.
- High-speed operation.
- Minimal energy consumption.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
One of the primary reasons industries choose centrifugal pumps is their affordability. They have a relatively simple design, which translates to lower manufacturing and maintenance costs.
Cost Benefits:
- Lower initial purchase price.
- Reduced maintenance and repair expenses.
- Energy-efficient operation lowers utility costs.
3. Versatility Across Industries
Centrifugal pumps can handle various fluids, including water, chemicals, and slurries. Their adaptability makes them suitable for numerous industrial applications, from food processing to petrochemicals.
Common Applications:
- Water supply and treatment.
- Chemical manufacturing.
- Oil and gas refineries.
4. Ease of Installation and Maintenance
The straightforward design of centrifugal pumps simplifies both installation and maintenance. With fewer moving parts, the risk of mechanical failure is minimized.
Maintenance Advantages:
- Simple disassembly for cleaning and repairs.
- Availability of spare parts from suppliers like Calama Pumps.
- Lower downtime due to quick servicing.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Centrifugal Pump
Selecting the right centrifugal pump for your industrial application requires careful evaluation of several factors. Understanding these considerations ensures you get the best performance and longevity from your equipment.
1. Flow Rate Requirements
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or cubic meters per hour (m³/h), determines how much fluid the pump can move. Matching the pump’s capacity to your operational needs prevents underperformance or overexertion.
How to Assess:
- Calculate your system’s peak demand.
- Consider variations in fluid volume over time.
- Choose a pump with a flow rate slightly above your maximum requirement.
2. Pressure and Head
The pressure the pump needs to generate to move fluid through the system is crucial. Head refers to the height the pump can push the fluid, and it impacts the pump’s efficiency.
Factors to Evaluate:
- Total dynamic head (TDH) of your system.
- Friction losses in piping and fittings.
- Vertical lift and discharge distance.
3. Type of Fluid
The nature of the fluid being pumped affects the pump’s material and design. Viscous, corrosive, or abrasive fluids require specialized impellers and casings.
Fluid Considerations:
- Temperature and chemical composition.
- Viscosity and particle content.
- Compatibility with pump materials.
4. Pump Efficiency
Energy-efficient pumps lower operational costs and reduce environmental impact. Evaluating the pump’s efficiency curve helps determine its performance across various flow rates and pressures.
Efficiency Tips:
- Select pumps with high-efficiency ratings.
- Monitor performance metrics like power consumption.
- Partner with suppliers like Calama Pumps for energy-efficient options.
5. Durability and Construction
Industrial environments demand robust equipment. The pump’s construction material must withstand harsh conditions, including high temperatures and corrosive chemicals.
Material Choices:
- Stainless steel for chemical resistance.
- Cast iron for durability in heavy-duty applications.
- Specialized alloys for high-temperature operations.
6. Supplier Reputation and Support
Choosing a reputable supplier ensures you receive high-quality equipment and reliable after-sales service. Trusted names like Calama Pumps offer expert advice, genuine spare parts, and comprehensive support.
Why Supplier Matters:
- Access to certified and tested equipment.
- Technical support for installation and maintenance.
- Warranty and service agreements.
Why Calama Pumps Recommend Centrifugal Pumps
Calama Pumps has established itself as a leading provider of industrial pumping solutions, and centrifugal pumps remain one of their top recommendations. Their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility align perfectly with Calama Pumps’ commitment to quality and performance.
Reasons for Recommendation:
- Proven reliability in diverse industrial applications.
- Availability of customizable solutions.
- Strong after-sales support and maintenance services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why are centrifugal pumps so popular in industrial use?
Their efficiency, affordability, and ability to handle various fluids make them a preferred choice for industrial applications.
What types of fluids can centrifugal pumps handle?
Centrifugal pumps can move water, chemicals, oils, and slurries, making them versatile across industries.
How do I choose the right centrifugal pump for my needs?
Assess flow rate, pressure requirements, fluid type, and system head to select a pump that meets your specifications.
Are centrifugal pumps energy-efficient?
Yes, their high efficiency reduces power consumption, lowering operational costs.
Why trust Calama Pumps for centrifugal pump solutions?
Calama Pumps offers high-quality, efficient centrifugal pumps with expert support and reliable service.
Centrifugal pumps continue to dominate industrial applications due to their efficiency, affordability, and adaptability. By partnering with reputable suppliers like Calama Pumps, businesses ensure they receive high-performance equipment tailored to their specific needs.
Caterories
- No category available.
Subscribe
Subscribe to Our newsletter for free Update every week
